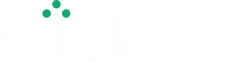
Get A Quote
What is Rotavirus?
2024-03-27
Rotavirus is a highly contagious virus that primarily affects infants and young children, causing severe diarrhea and vomiting. It spreads through contact with contaminated feces, surfaces, or objects, and can lead to dehydration and other complications, particularly in young children. Vaccination is available to prevent rotavirus infections.
Symptoms
The syndrome associated with contracting the rotavirus typically involves symptoms such as severe watery diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal pain. These symptoms can lead to dehydration, which is particularly dangerous in infants and young children. In some cases, rotavirus infection may also cause respiratory symptoms such as coughing and a runny nose. It's essential to seek medical attention if you suspect a rotavirus infection, especially in young children or individuals with weakened immune systems.
Causes
Rotavirus can be found in the stool of an infected individual up to two days before symptoms begin and for approximately 10 days afterward as symptoms subside. During this period, the virus can easily spread through hand-to-mouth contact, even if the infected person is not showing symptoms.
If proper hand hygiene is not practiced, particularly after using the toilet or changing diapers, the virus can contaminate surfaces and objects such as food, toys, and utensils. Transmission can occur if another person touches contaminated surfaces and then touches their mouth. The virus can remain viable on surfaces for an extended period if not properly disinfected.
Although it's possible to contract rotavirus multiple times, including after vaccination, subsequent infections are usually milder in severity.

Photo from freepik.com
ROTA is widely infected by young children through fecal-oral route
Rotavirus infections can occur worldwide, but they are most prevalent in areas with inadequate sanitation, limited access to clean water, and crowded living conditions. This is because the virus spreads through the fecal-oral route, meaning it is transmitted when people come into contact with contaminated fecal matter and then touch their mouths or consume contaminated food or water. Therefore, populations with poor hygiene practices and limited access to proper sanitation facilities are at higher risk of infection. Additionally, infants and young children (aged 3-35 months) are particularly susceptible to rotavirus infection due to their immature immune systems and frequent hand-to-mouth behaviors.
How to detect ROTA
-
Feces Antigen Tests: These tests detect rotavirus antigens in stool samples using immunoassay techniques. They are rapid, simple, and effective for diagnosing rotavirus infections.
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR tests can detect the presence of rotavirus RNA in stool samples with high sensitivity and specificity. They are especially useful for confirming rotavirus infections in cases where antigen tests yield inconclusive results.
-
Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA): EIA tests detect rotavirus antigens in stool samples using specific antibodies. They are relatively simple and provide rapid results, making them suitable for use in clinical settings.
-
Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA): IFA tests use fluorescently labeled antibodies to detect rotavirus antigens in stool samples. They offer high sensitivity and specificity and are commonly used in clinical laboratories.
AICHEK's Solution
We offer the Rotavirus Rapid Test Kit for Fecal Antigen Testing, boasting impressive statistics:
- Relative Sensitivity: 99.1% (with a 95% Confidence Interval of 96.8%-99.9%)
- Relative Specificity: 100% (with a 95% Confidence Interval of 97.7%-100.0%)
- Overall Agreement: 99.5% (with a 95% Confidence Interval of 98.1%-99.9%)