Get A Quote
How Does COVID Test Work?
Although the scourge of covid 19 is gradually leaving us, there is still a significant proportion of people who will be re-infected by the virus and many people still don’t know how does the covid test work. It makes sense to keep a supply of covid 19 test kit at home. Let me tell you how does covid test work ?
How Does the Covid Test Work?
In the realm of virus detection, there exist two primary diagnostic tests geared to identify the presence of viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, the culprit behind Covid-19. Diagnostic tests essentially unveil whether an individual is currently infected and are the focus of programs like the UK's contact tracing initiatives.
Beyond these, there are antibody tests, also known as serology tests, adept at revealing whether someone has encountered the virus previously, though they do not ascertain the current status of infection.
Now, delving into the specifics, the diagnostic arena boasts two main players: PCR tests and antigen tests. These tests stand as vital tools in the battle against infectious diseases, offering crucial insights into individuals' infection statuses and aiding in the containment efforts. Let me show you how do pcr test work and how does covid antigen test work.
Now, delving into the specifics, the diagnostic arena boasts two main players: PCR tests and antigen tests. These tests stand as vital tools in the battle against infectious diseases, offering crucial insights into individuals' infection statuses and aiding in the containment efforts. Let me show you how do pcr test work and how does covid antigen test work.
What is PCR Test ?
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests are a fast, highly accurate way to diagnose certain infectious diseases and genetic changes. The tests work by finding the DNA or RNA of a pathogen (disease-causing organism) or abnormal cells in a sample.
How Do PCR Test Work?
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests stand as a cornerstone in virus detection, capable of identifying the virus's RNA (genetic material) within a sample. The process kicks off with a concoction of substances introduced into the sample, often obtained from a nose or throat swab. These substances, namely "reverse transcriptase" and "DNA polymerase," get to work by replicating any viral RNA within the sample, creating an abundance of copies.
The magic lies in these multiplied copies, ensuring there are enough of them to be easily detected during subsequent testing. The testing phase employs specially crafted "primers" and "probes" meticulously designed to lock onto specific sequences within the virus's genetic code. These primers are akin to expert detectives, honing in on unique segments of the virus's genome, akin to finding a needle in a haystack. Once these primers and probes spot the targeted genetic material, they send out a clear signal, confirming the presence of the virus.
In essence, PCR tests function as genetic detectives, using their keen molecular senses to pinpoint the virus's genetic material within a given sample, allowing for accurate and swift identification.
What is Antigen Test?
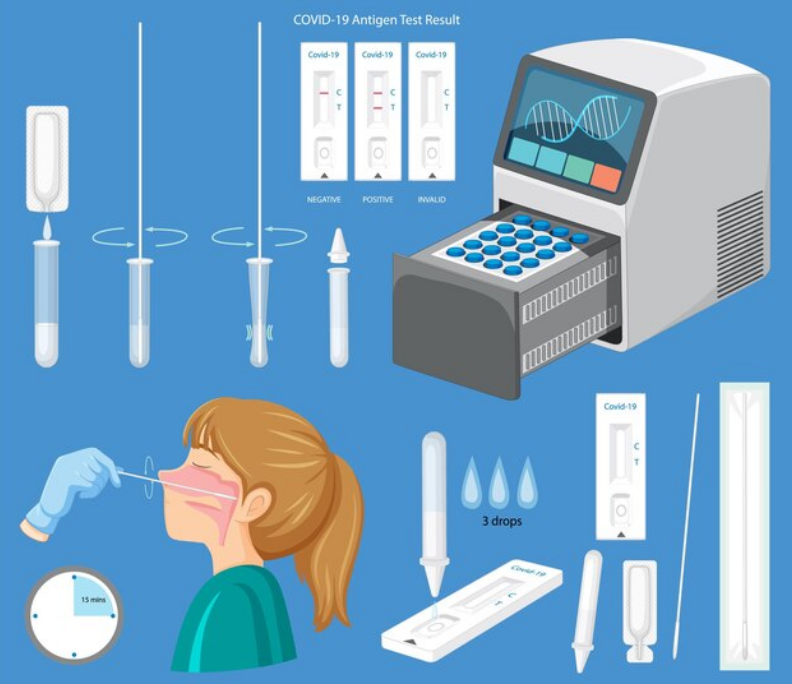
Antigen tests are designed to spot antigens in the body, these being substances that trigger immune responses, like the release of antibodies. The immune system, with its vigilant antibodies, detects these antigens. Rapid antigen detection tests operate on this fundamental principle. By now, a multitude of individuals have undergone antigen tests, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, or even both to diagnose COVID-19. Usually, these tests entail a swab taken from the nose or throat.
How Does Covid Antigen Test Work?
Antigen tests, in contrast to their PCR counterparts, don't hunt for the virus's genetic material; instead, they typically seek out specific proteins within the virus. When antigens are detected, they usually trigger an immune response in the body, indicating the presence of the virus.
However, these terms are often used interchangeably, causing confusion among many. According to Professor Eleanor Riley, an esteemed expert in Immunology and Infectious Disease at the University of Edinburgh, the terminology can be perplexing. She explains, "Tests referred to as 'antigen' tests are primarily looking for a component of the virus, usually its external protein coat, which triggers the immune response. However, the COVID-19 test we use actually detects viral RNA, a genetic component, which is not technically a viral antigen."
Therefore, when people mention "antigen" tests and others discuss tests for viral RNA or "PCR tests," they are essentially referring to the same fundamental concept. It's a bit like different roads leading to the same destination, albeit with unique signposts.
How Does a Positive Covid Test Look?
PCR tests, short for Polymerase Chain Reaction tests, play a pivotal role in COVID-19 diagnostics. In the PCR process, genetic material from the patient's sample is amplified, making even tiny amounts of coronavirus genes detectable. A healthcare professional first converts the RNA from the sample into double-stranded DNA using an enzyme. This DNA is then mixed with a solution containing polymerase, an enzyme that facilitates DNA replication.
Under carefully controlled conditions, the DNA strands are separated and copied using primers, ensuring that only coronavirus DNA is replicated. This meticulous amplification process results in multiple copies of coronavirus DNA, allowing for accurate detection.
On the other hand, antigen tests rely on the body's immune response to identify the presence of SARS-CoV-2. Antigens are substances that trigger the production of antibodies in the body. In antigen testing, the patient's sample is treated with a solution containing salt and soap to break down cells and particles.
This treated sample is then applied to a test strip containing specific antibodies designed to recognize SARS-CoV-2 antigens. If coronavirus antigens are present in the sample, they bind with the antibodies on the test strip, leading to the appearance of a visible line. The presence of this line indicates a positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
While PCR tests offer high accuracy, they require sophisticated laboratory procedures and can take time to produce results. In contrast, antigen tests provide faster results, making them valuable for quick screening, although they may be less sensitive than PCR tests.
Both types of tests serve essential roles in detecting and managing COVID-19 infections, allowing healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care and public health measures.
Conclusion
Understanding the benefits and limitations of PCR and antigen testing and when to use them can help control the COVID-19 pandemic. So the next time you get tested for COVID-19, choose the test that's right for you. If you want to know more, come to AICHEK for a consultation!