Get A Quote
Lateral Flow Rapid Tests in Combating Malaria
Source: https://www.wanda.be/en/a-z-index/malaria-world-map
Malaria remains a significant global health challenge, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare resources.
High Transmission Areas:
Sub-Saharan Africa: This region has the highest transmission rates and accounts for the majority of global malaria cases and deaths. Countries such as Nigeria, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, and Mozambique are particularly affected.
South Asia: Countries like India and Pakistan have significant malaria transmission, particularly in rural and semi-rural areas.
Southeast Asia: Areas in countries like Myanmar, Indonesia, and parts of Thailand face malaria risks.
Latin America: Some areas in Brazil, Colombia, and Peru report malaria cases, particularly in the Amazon basin.
Diagnosis
Microscopic Examination:
Blood Smear: This is the gold standard for malaria diagnosis. A drop of the patient's blood is placed on a microscope slide, stained (commonly with Giemsa stain), and examined under a microscope for the presence of malaria parasites. This method allows for the identification of the specific species of Plasmodium (e.g., P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae) and the determination of parasite density.
Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs):
RDTs detect specific antigens produced by malaria parasites. These tests are easy to use and can provide results in about 15-20 minutes. They are particularly useful in areas where microscopic examination is not feasible.
Molecular Diagnosis:
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This method is highly sensitive and specific, capable of detecting low levels of malaria parasites in the blood. PCR is mainly used in research settings or when a definitive diagnosis is needed, especially for mixed infections or when the species identification is unclear.
Current Challenges in Malaria Diagnosis
Limited Access to Laboratory Facilities:
In many malaria-endemic regions, access to laboratory facilities for traditional diagnostic methods such as microscopy is limited, delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Symptom Overlap with Other Diseases:
Malaria symptoms can overlap with those of other febrile illnesses, leading to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment.
Need for Rapid and Accurate Diagnosis:
Timely diagnosis is crucial for effective malaria management, especially in severe cases where delays can result in complications or death.
The use of lateral flow rapid tests (LFTs) presents a promising approach to improving malaria diagnosis and management in resource-constrained settings. This article examines the application of LFTs in the fight against malaria, assessing their effectiveness, challenges, and future prospects.
Role of Lateral Flow Rapid Tests
Rapid Results:
LFTs provide results within minutes, enabling healthcare workers to promptly initiate appropriate treatment and prevent disease progression.
Ease of Use:
These tests require minimal training and equipment, making them suitable for use in remote areas with limited healthcare infrastructure.
High Sensitivity and Specificity:
Modern LFTs exhibit high sensitivity and specificity, ensuring accurate detection of malaria parasites even at low levels of infection.
Point-of-Care Testing:
LFTs facilitate point-of-care testing, allowing for immediate diagnosis and treatment decisions directly at the patient's bedside or in community health settings.
Challenges and Limitations
Variability in Performance:
The performance of LFTs can vary depending on factors such as the brand, lot-to-lot consistency, and environmental conditions, affecting their reliability in field settings.
Detection of Low Parasite Density:
LFTs may have reduced sensitivity in detecting low parasite densities compared to molecular diagnostic methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Quality Assurance and Training:
Ensuring the quality and accuracy of LFT results requires ongoing training of healthcare workers and implementation of quality control measures.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Improved Sensitivity and Specificity:
Ongoing research aims to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of LFTs through the development of novel detection methods and improved assay designs.
Multiplexing Capabilities:
Future LFTs may incorporate multiplexing capabilities to detect multiple malaria parasite species or differentiate between malaria and other febrile illnesses in a single test.
Digital Integration:
Integration with digital technologies, such as smartphone-based result interpretation and data transmission, could enhance the usability and accessibility of LFTs in remote settings.
Conclusion
Lateral flow rapid tests offer a valuable tool in the fight against malaria by providing rapid and accessible diagnostic solutions in resource-limited settings. While they have demonstrated significant benefits in improving diagnosis and patient management, challenges remain in ensuring their consistent performance and accuracy. Continued research and innovation are essential to further enhance the capabilities of LFTs and maximize their impact on malaria control efforts worldwide.
AICHEK's Solution
99.9% Accuracy of Rapid Malaria Antigen Test
Our malaria antigen test kit can reach at an accuracy at 95%, it can fully meet the requirement of WHO, that the overall sensitivity should be around 95%. So our malaria test kit can provide users an authentic result which is more accurate than similar malaria blood tests in the market.
Relative Sensitivity for P.f.-specific antigens: 80/80> 99.9% (95.4%~100.0%)*
Relative Specificity: 451/451>99.9% (99.2%~100.0%)*
Performance: (80+451)/(80+451)=581/581=99.9% (99.3%~100.0%)*
- 95% Confidence Interval
Ordering Information
| Cat No | Product | Format | Packing | Specimen | Read Time | Certificate |
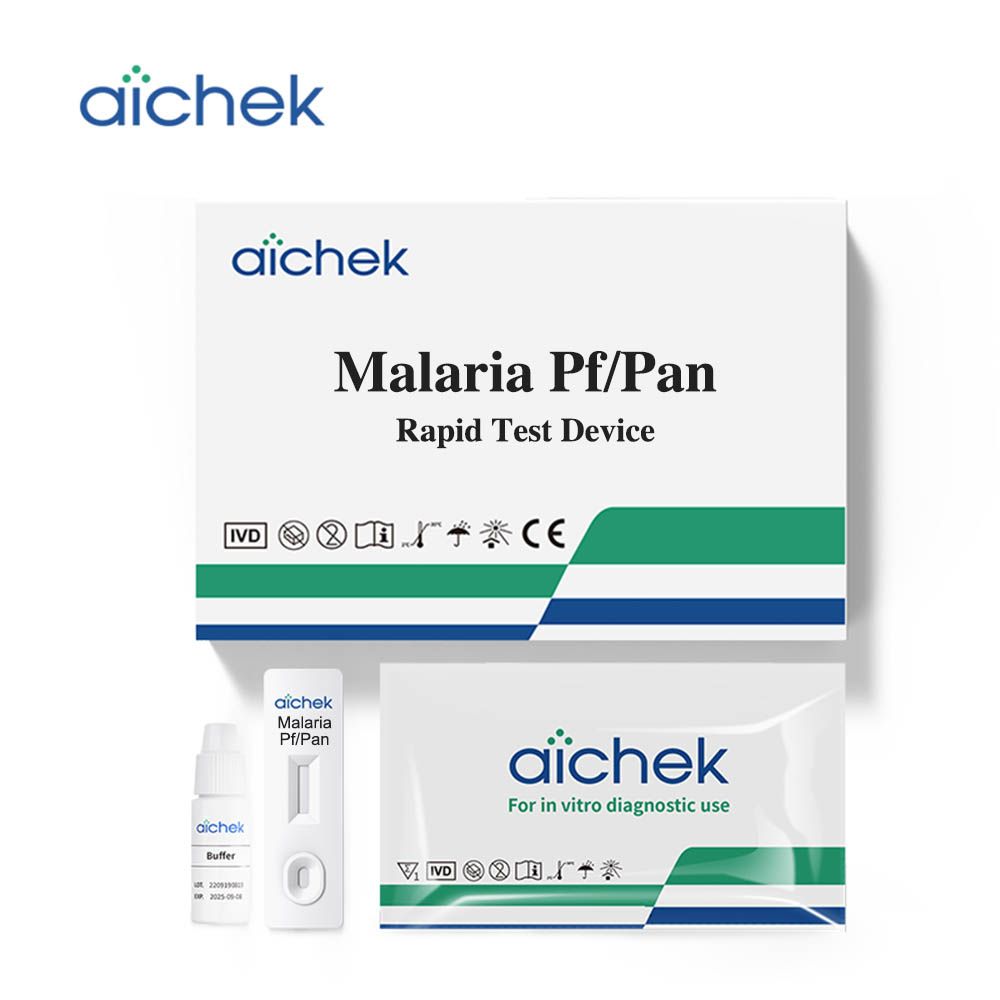
| MAL-D22a | Malaria Pf /Pan Rapid Test Device Test+Buffer | Cassette | 25T/BOX | Whole Blood | 10min- | CE |
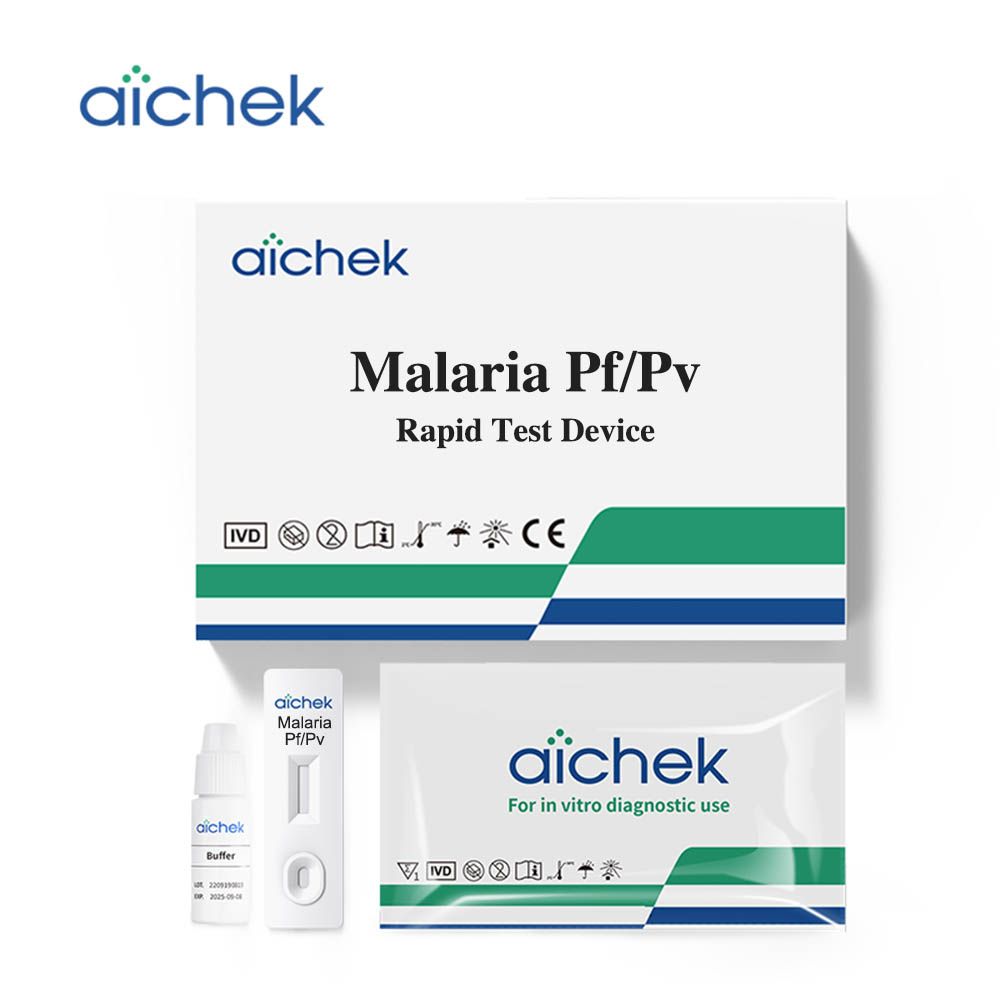
| MAL-D22b | Malaria Pf /Pv Rapid Test Device Test+Buffer | Cassette | 25T/BOX | Whole Blood | 10min- | CE |
| MAL-D02c | Malaria Pf Rapid Test Device Test+Buffer | Cassette | 25T/BOX | Whole Blood | 10min- | CE |